EXHIBIT 99.1
Published on November 2, 2023
Exhibit 99.1

Ocuphire Corporate Presentation November 2023

This presentation contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of
the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such statements include, but are not limited to, statements concerning the success and timing of planned regulatory filings and approvals, pre-commercial activities, commercialization
strategy and timelines, business strategy, product labels, cash runway, scalability, future clinical trials in presbyopia (P), dim light/night vision disturbance (DLD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) / diabetic macular edema (DME), including
the potential for Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution (POS) to be a “best in class” presbyopia drop, and timing of planned future clinical trials for APX3330, APX2009 and APX2014, the advancement to Phase 3 registration path for APX3330, FDA
agreement on Special Protocol Assessment, the success and timing of planned regulatory filings, business strategy, cash runway, scalability, the potential for APX3330 to be the most advanced and the first line of therapy for DR patients, and
the potential market opportunity for and the ability of APX3330 to slow DR progression. These forward-looking statements are based upon the Company’s current expectations and involve assumptions that may never materialize or may prove to be
incorrect. Actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements as a result of various risks and uncertainties, including, without limitation: (i) the success, costs, and
timing of regulatory submissions and pre-clinical and clinical trials, including enrollment and data readouts; (ii) regulatory requirements or developments; (iii) changes to clinical trial designs and regulatory pathways; (iv) changes in
capital resource requirements; (v) risks related to the inability of Ocuphire to obtain sufficient additional capital to continue to advance its product candidates and its preclinical programs; (vi) legislative, regulatory, political and
economic developments, (vii) changes in market opportunities, (viii) risks that the partnership with Viatris may not facilitate the commercialization or market acceptance of Ocuphire’s product candidates; (ix) the success and timing of
commercialization of any of Ocuphire’s product candidates, including the scalability of Ocuphire’s product candidates and (x) the maintenance of Ocuphire’s intellectual property rights. The foregoing review of important factors that could
cause actual events to differ from expectations should not be construed as exhaustive and should be read in conjunction with statements that are included herein and elsewhere, including the risk factors detailed in documents that have been
and may be filed by the Company from time to time with the SEC. All forward-looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date on which they were made. The Company undertakes no obligation to update such statements to
reflect events that occur or circumstances that exist after the date on which they were made. The Company makes no representation or warranty, express or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in or
incorporated by reference into this presentation. Nothing contained in or incorporated by reference into this presentation is, or shall be relied upon as, a promise or representation by the Company as to the past or future. The Company
assumes no responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of any such information. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market shares and other data about our
industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. The trademarks included herein are the property of the owners thereof and are used for reference purposes
only. Such use should not be construed as an endorsement of such products. Disclosures and Forward-Looking Statements
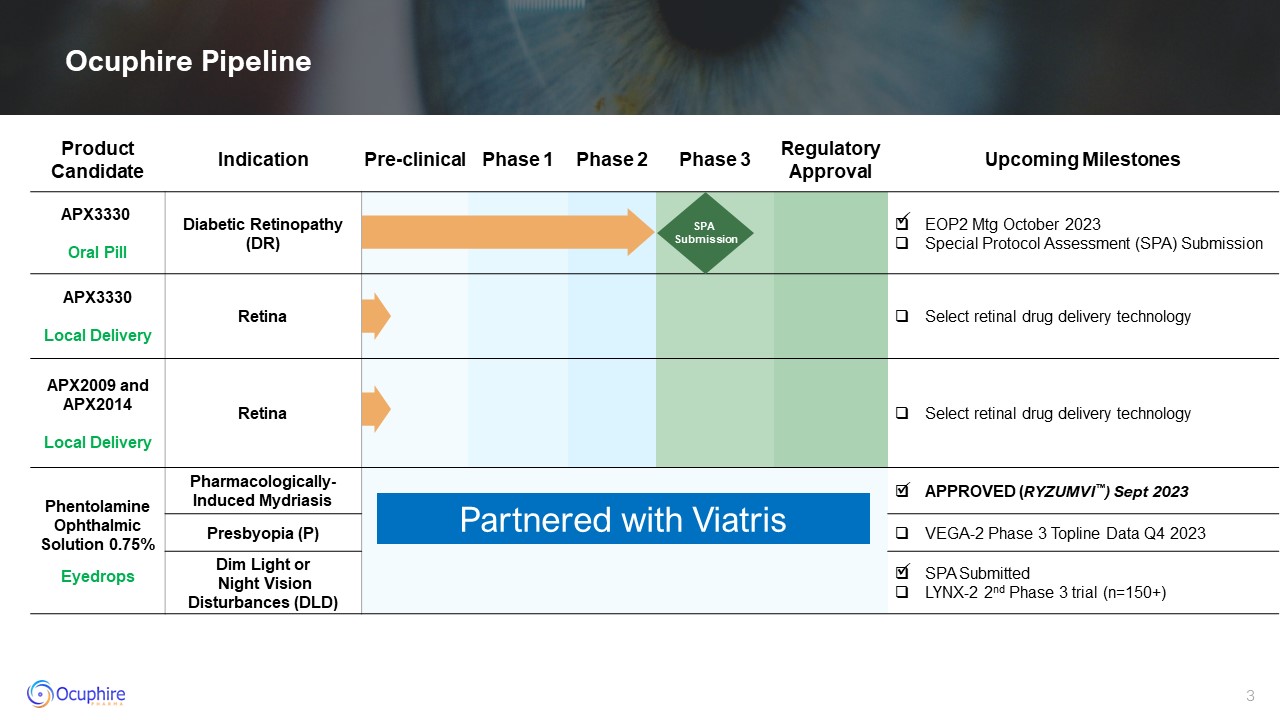
Ocuphire Pipeline Product Candidate Indication Pre-clinical Phase 1 Phase
2 Phase 3 Regulatory Approval Upcoming Milestones APX3330 Oral Pill Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) EOP2 Mtg October 2023 Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) Submission APX3330 Local Delivery Retina Select retinal drug delivery
technology APX2009 and APX2014 Local Delivery Retina Select retinal drug delivery technology Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% Eyedrops Pharmacologically-Induced Mydriasis APPROVED (RYZUMVI™) Sept 2023 Presbyopia (P) VEGA-2
Phase 3 Topline Data Q4 2023 Dim Light or Night Vision Disturbances (DLD) SPA Submitted LYNX-2 2nd Phase 3 trial (n=150+) SPA Submission Partnered with Viatris

Management Team with Decades of Drug Development Experience Drey ColemanVP,
Clinical Operations Amy Rabourn, CPA SVP, Finance Charlie Hoffmann, MBA SVP, Corporate Development Mitch Brigell, PhD Head, Clinical Development and Strategy Daniela Oniciu, PhD Global Head, R&D, Chemistry and Product
Development Ronil Patel, MTech, MS SVP, Operations and BD Chris Ernst Global Head, QA and Manufacturing Barbara Withers, PhDVP, Clinical and Regulatory Strategy Bindu Manne Head, Market Development and Commercialization Laura
Gambino Director, Project Management George Magrath, MD, MBA CEO

Corporate Highlights Late-Stage Clinical Candidate for Retinal Diseases
Represents Multi-Billion Dollar Opportunity Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% (POS) for Refractive Disorders Global license agreement with Viatris to fund all development and commercialization for phentolamine indications: RYZUMVI™
(Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution) 0.75% for the treatment of pharmacologically-induced mydriasis received FDA approval in September 2023 Approval triggered $10M milestone payment Presbyopia and Dim Light Disturbances currently in Phase
3 Experienced Retina Drug Development Team to Advance APX3330 into Phase 3 APX3330: Paradigm Changing, Non-invasive, Safe Oral Tablet for millions of NPDR patients that are currently left untreated Ref-1, a novel, dual target
(angiogenesis and inflammation) for retinal diseases ZETA-1 Phase 2 showed APX3330 prevented or slowed progression of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Successful EOP2 meeting with the FDA and a Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) to be submitted

Diabetic Retinopathy Market and Unmet Need
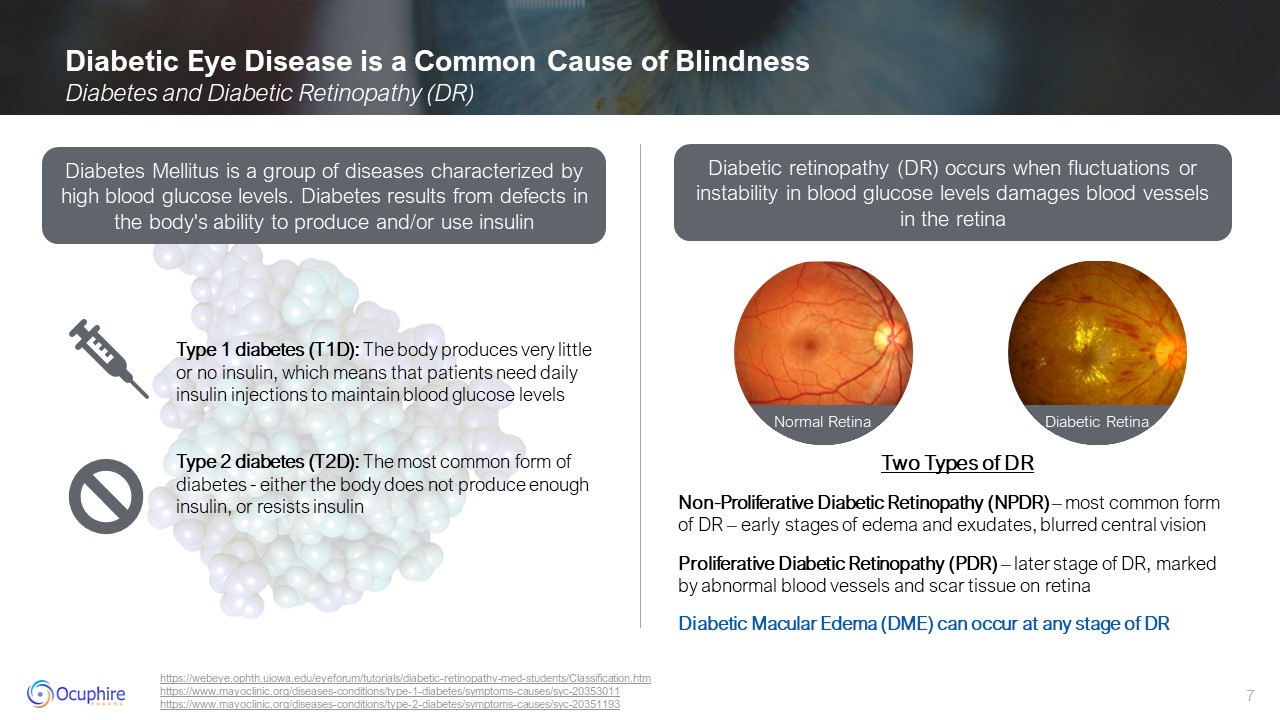
Diabetic Eye Disease is a Common Cause of Blindness Diabetes and Diabetic
Retinopathy (DR) https://webeye.ophth.uiowa.edu/eyeforum/tutorials/diabetic-retinopathy-med-students/Classification.htm https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-1-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20353011
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193 Two Types of DR Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) – most common form of DR – early stages of edema and exudates, blurred central
vision Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) – later stage of DR, marked by abnormal blood vessels and scar tissue on retina Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) can occur at any stage of DR Diabetes Mellitus is a group of diseases
characterized by high blood glucose levels. Diabetes results from defects in the body's ability to produce and/or use insulin Diabetic retinopathy (DR) occurs when fluctuations or instability in blood glucose levels damages blood vessels in
the retina Type 1 diabetes (T1D): The body produces very little or no insulin, which means that patients need daily insulin injections to maintain blood glucose levels Type 2 diabetes (T2D): The most common form of diabetes - either the
body does not produce enough insulin, or resists insulin Normal Retina Diabetic Retina

American Diabetes Association; International Diabetes Federation; Healthline;
*Ocuphire internal analysis and assumptions Das UN. DME, retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration as inflammatory conditions. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12(5):1142-1157. doi:10.5114/aoms.2016.61918 Patient survey adapted from Lions
International Foundation and International Diabetes Foundation-Europe; Meltzer 2000 Guidehouse Triangulation of Global Data, Market Scope and Investor Forecasts (2020) AMD = Age-Related Macular Degeneration; DME = Diabetic Macular Edema ;
BRVO = Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention & Health Promotion. Health & economic costs of chronic diseases. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, US Department of Health
and Human Services; 2018 Four-Year Visual Outcomes in a Randomized Trial of Intravitreous Aflibercept for Prevention of Vision Threatening Complications of Diabetic Retinopathy (Protocol W).” JAMA. February 7, 2023 Diabetic Retinopathy at a
Glance Current Treatment Landscape Demonstrates Need for Non-Invasive Therapies The number of people with DR expected to increase more than 14M by 2050 There are ~8M adults in the U.S. with NPDR DR is the leading cause of blindness among
working-age adults with the median age of onset at 45 – 50 years Majority of moderate to severe patients with DR are not treated with anti-VEGF due to injection burden and no benefit to visual acuity Prevention of Progression is favored by
payors with chronic diseases such as diabetes which is the primary driver of increased healthcare costs Physicians have no non-invasive options for NPDR with current standard being wait-and-monitor
American Diabetes Association; International Diabetes Federation; Healthline;
*Ocuphire internal analysis and assumptions; Spherix Global Insights Patient survey adapted from Lions International Foundation and International Diabetes Foundation-Europe; Meltzer 2000 Estimates are provided by the National Eye Institute,
FactSheet, Global Data, and Research and Markets. Estimated values are rounded. Estimated prevalence in the U.S.; DME- Diabetic Macular Edema; Age-related Macular Degeneration; Geographic Atrophy; Retinal Vein Occlusion U.S Diabetic
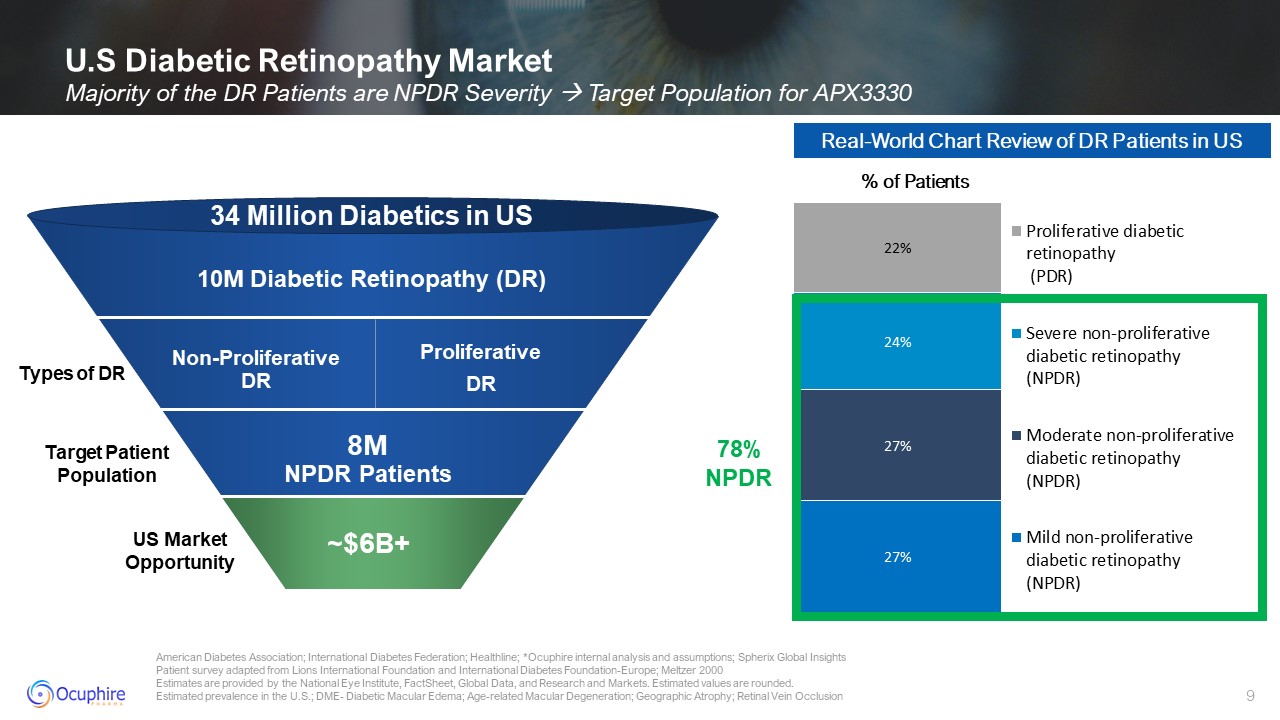
Retinopathy Market Majority of the DR Patients are NPDR Severity Target Population for APX3330 10M Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) 34 Million Diabetics in US 8MNPDR Patients US Market Opportunity Target Patient
Population ~$6B+ 78% NPDR Non-Proliferative DR Proliferative DR Real-World Chart Review of DR Patients in US % of Patients Types of DR
Spherix Global Insights: DR Market DYNAMIX October 2022 Early treatment
diabetic retinopathy study research group. ophthalmology. 1991;98(5 suppl):823-33. Diabetes control and complications trial research group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):997-86. Fathy C, Patel S, Sternberg P Jr, Kohanim S. Disparities in
adherence to screening guidelines for diabetic retinopathy in the United States: a comprehensive review and guide for future directions. Semin Ophthalmol. 2016;31(4):364–377. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2016.1154170 Progression of DR Severity
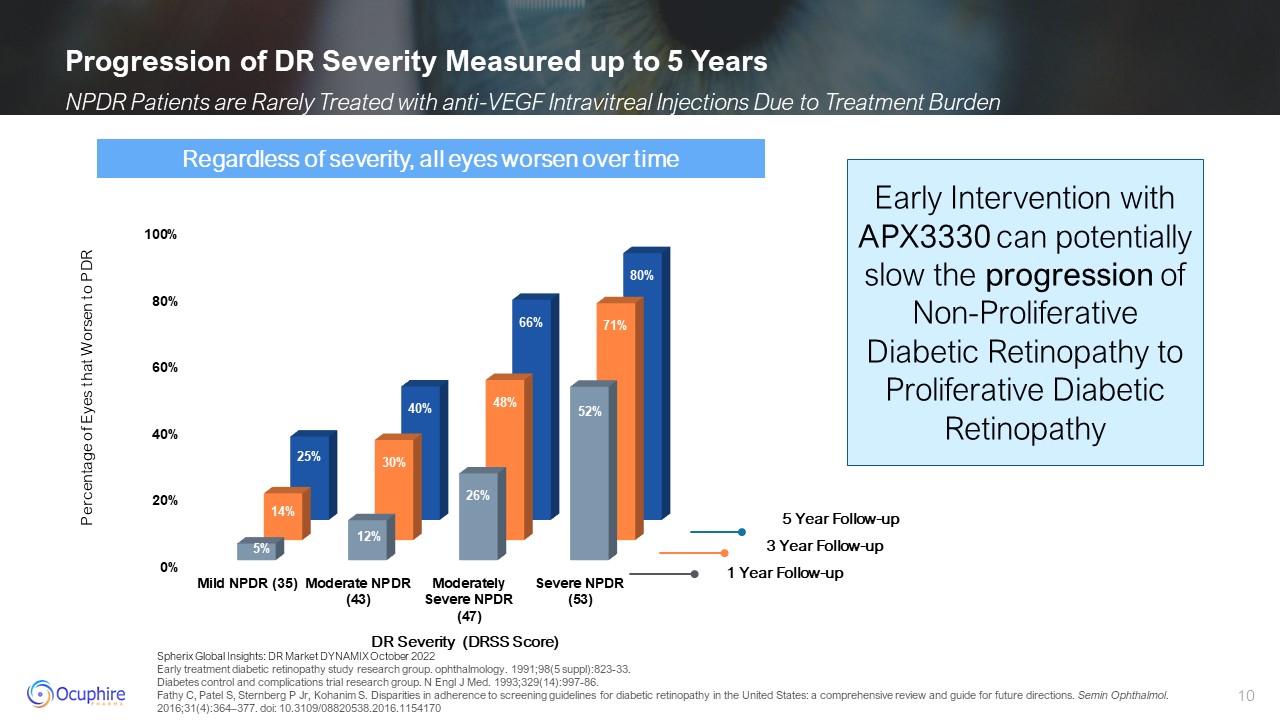
Measured up to 5 Years NPDR Patients are Rarely Treated with anti-VEGF Intravitreal Injections Due to Treatment Burden 1 Year Follow-up 3 Year Follow-up 5 Year Follow-up Percentage of Eyes that Worsen to PDR Regardless of severity, all
eyes worsen over time DR Severity (DRSS Score) Early Intervention with APX3330 can potentially slow the progression of Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy

Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Landscape
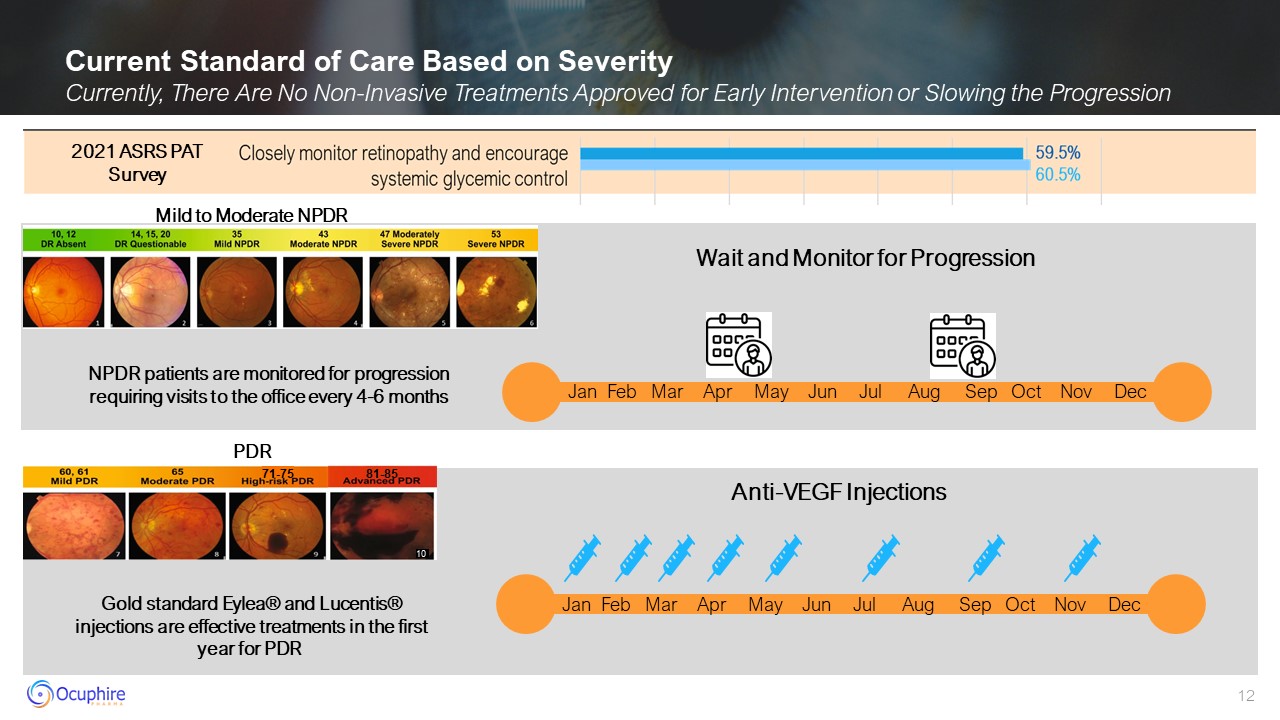
Current Standard of Care Based on Severity Currently, There Are No Non-Invasive
Treatments Approved for Early Intervention or Slowing the Progression Wait and Monitor for Progression Mild to Moderate NPDR Anti-VEGF
Injections PDR Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec 10 81-85 71-75 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec NPDR patients are monitored for progression requiring visits to the office every 4-6
months Gold standard Eylea® and Lucentis® injections are effective treatments in the first year for PDR 2021 ASRS PAT Survey
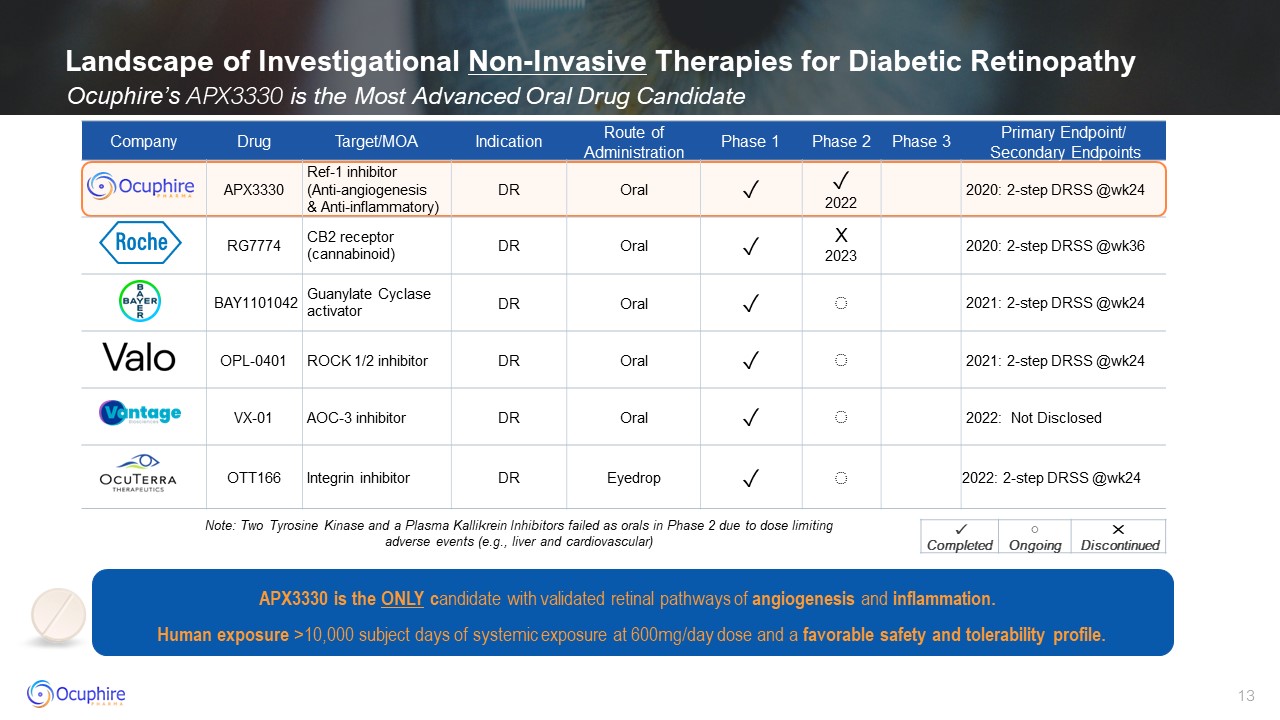
Landscape of Investigational Non-Invasive Therapies for Diabetic
Retinopathy Ocuphire’s APX3330 is the Most Advanced Oral Drug Candidate Company Drug Target/MOA Indication Route of Administration Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Primary Endpoint/ Secondary Endpoints APX3330 Ref-1
inhibitor (Anti-angiogenesis & Anti-inflammatory) DR Oral ✓ ✓ 2022 2020: 2-step DRSS @wk24 RG7774 CB2 receptor (cannabinoid) DR Oral ✓ X 2023 2020: 2-step DRSS @wk36 BAY1101042 Guanylate Cyclase
activator DR Oral ✓ ◌ 2021: 2-step DRSS @wk24 OPL-0401 ROCK 1/2 inhibitor DR Oral ✓ ◌ 2021: 2-step DRSS @wk24 VX-01 AOC-3 inhibitor DR Oral ✓ ◌ 2022: Not Disclosed OTT166 Integrin inhibitor DR Eyedrop ✓ ◌ 2022:
2-step DRSS @wk24 ✓ Completed ◌ Ongoing ✕ Discontinued Note: Two Tyrosine Kinase and a Plasma Kallikrein Inhibitors failed as orals in Phase 2 due to dose limiting adverse events (e.g., liver and cardiovascular) APX3330 is the ONLY
candidate with validated retinal pathways of angiogenesis and inflammation. Human exposure >10,000 subject days of systemic exposure at 600mg/day dose and a favorable safety and tolerability profile.
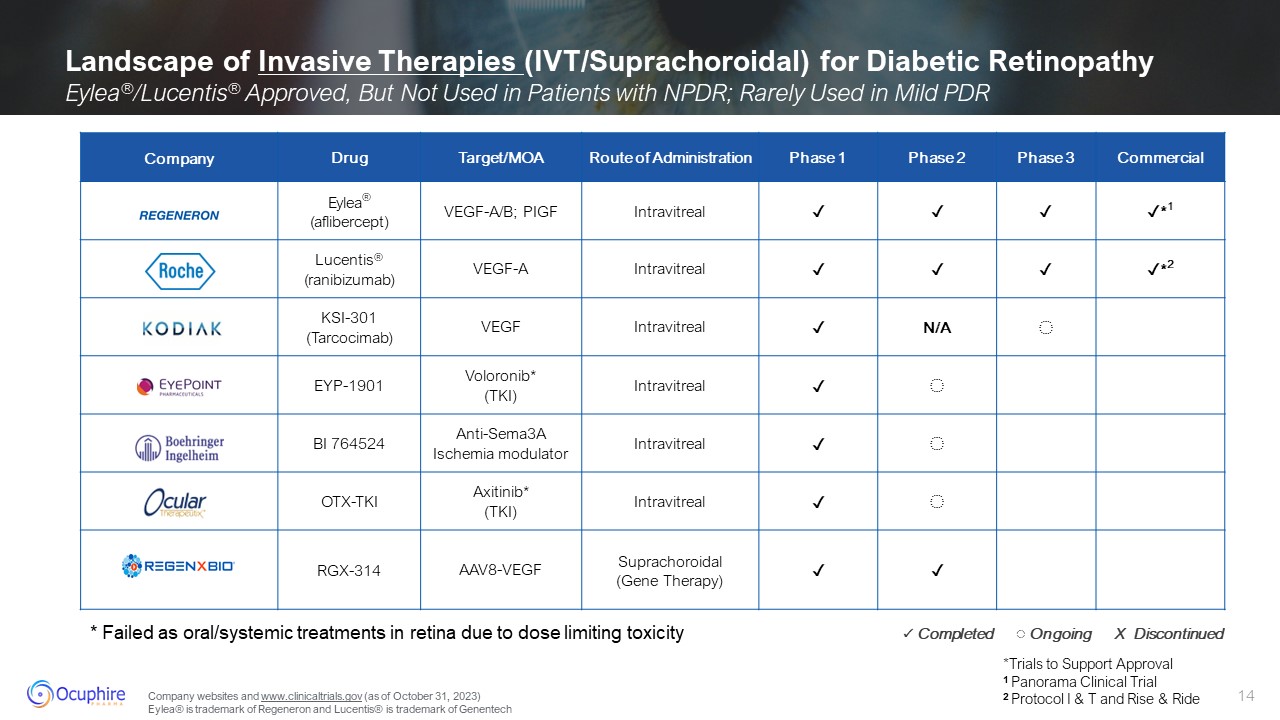
Landscape of Invasive Therapies (IVT/Suprachoroidal) for Diabetic Retinopathy
Eylea®/Lucentis® Approved, But Not Used in Patients with NPDR; Rarely Used in Mild PDR Company Drug Target/MOA Route of Administration Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Commercial Eylea® (aflibercept) VEGF-A/B;
PIGF Intravitreal ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓*1 Lucentis® (ranibizumab) VEGF-A Intravitreal ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓*2 KSI-301 (Tarcocimab) VEGF Intravitreal ✓ N/A ◌ EYP-1901 Voloronib* (TKI) Intravitreal ✓ ◌ BI 764524 Anti-Sema3A Ischemia
modulator Intravitreal ✓ ◌ OTX-TKI Axitinib* (TKI) Intravitreal ✓ ◌ RGX-314 AAV8-VEGF Suprachoroidal (Gene Therapy) ✓ ✓ *Trials to Support Approval 1 Panorama Clinical Trial 2 Protocol I & T and Rise & Ride ✓
Completed ◌ Ongoing X Discontinued * Failed as oral/systemic treatments in retina due to dose limiting toxicity Company websites and www.clinicaltrials.gov (as of October 31, 2023) Eylea® is trademark of Regeneron and Lucentis® is
trademark of Genentech

APX3330 Background
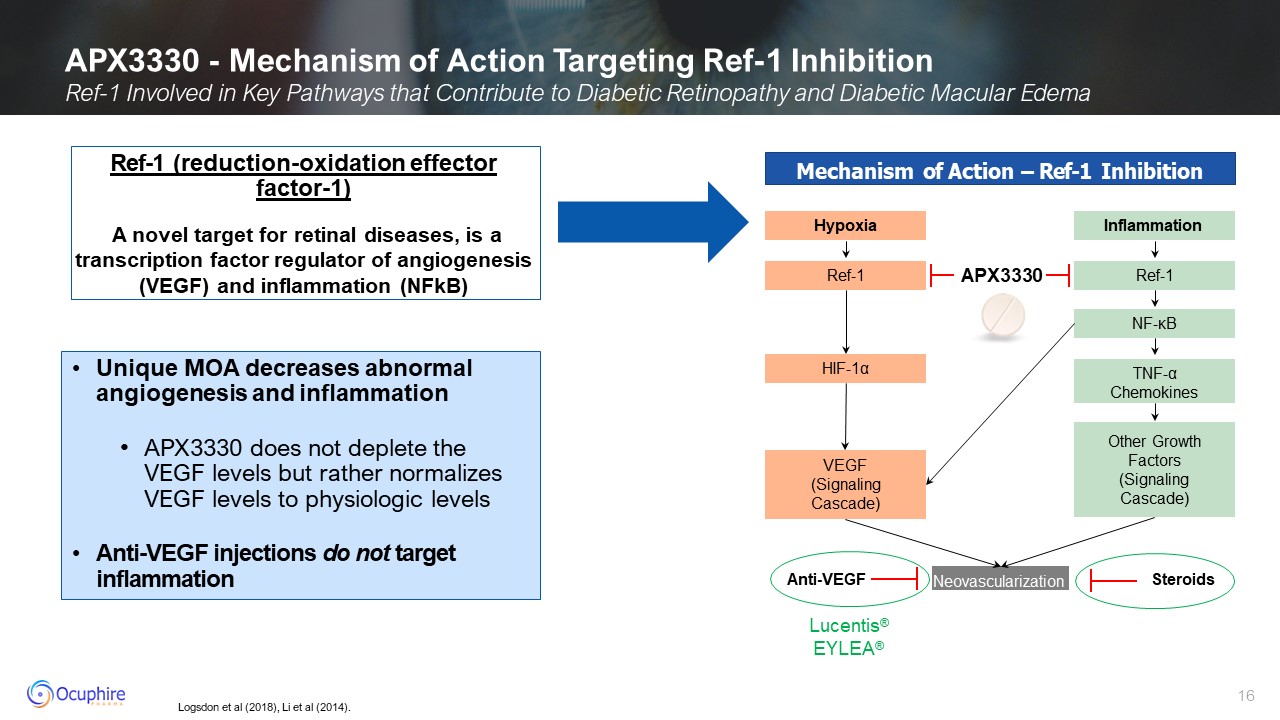
Logsdon et al (2018), Li et al (2014). APX3330 - Mechanism of Action Targeting
Ref-1 Inhibition Ref-1 Involved in Key Pathways that Contribute to Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Ref-1 (reduction-oxidation effector factor-1) A novel target for retinal diseases, is a transcription factor regulator of
angiogenesis (VEGF) and inflammation (NFkB) Mechanism of Action – Ref-1 Inhibition Hypoxia Ref-1 HIF-1α VEGF (Signaling Cascade) Inflammation Ref-1 NF-κB Other Growth Factors (Signaling
Cascade) TNF-α Chemokines Neovascularization Lucentis® EYLEA® Anti-VEGF Steroids APX3330 Unique MOA decreases abnormal angiogenesis and inflammation APX3330 does not deplete the VEGF levels but rather normalizes VEGF levels to
physiologic levels Anti-VEGF injections do not target inflammation
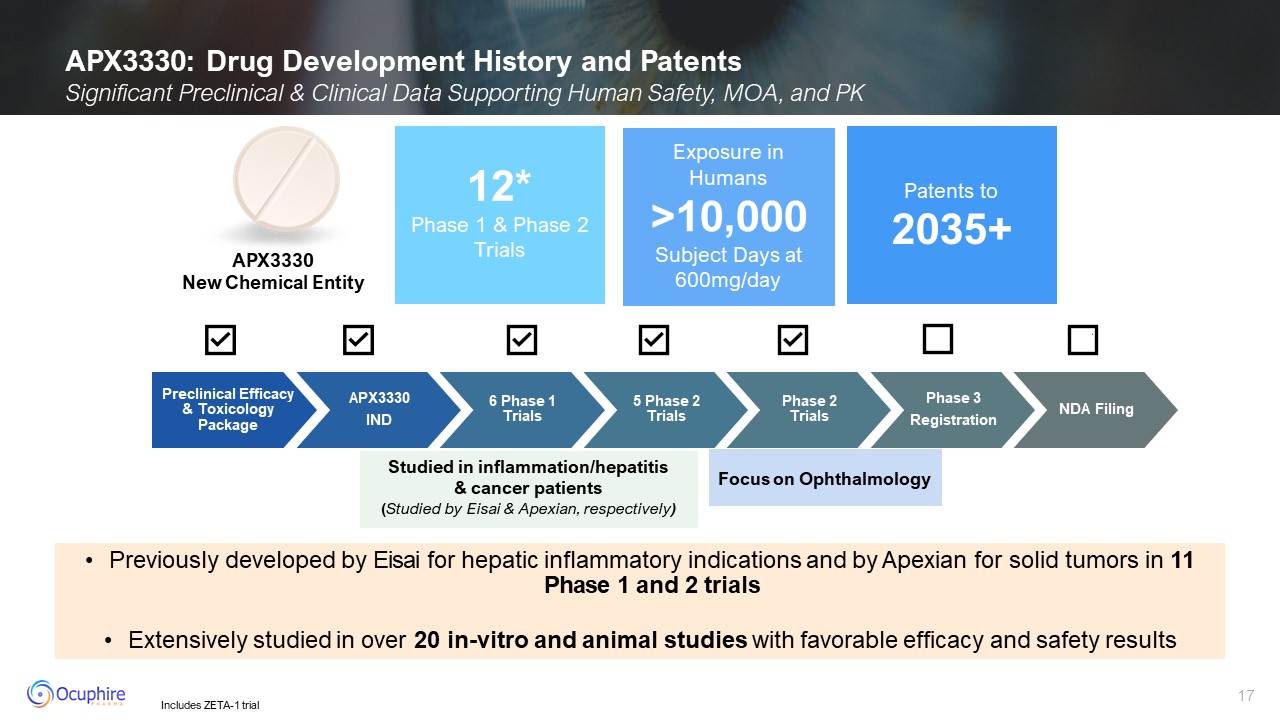
APX3330: Drug Development History and Patents Significant Preclinical &
Clinical Data Supporting Human Safety, MOA, and PK 12* Phase 1 & Phase 2 Trials Exposure in Humans >10,000 Subject Days at 600mg/day Patents to2035+ Studied in inflammation/hepatitis & cancer patients (Studied by Eisai
& Apexian, respectively) APX3330 New Chemical Entity Preclinical Efficacy & Toxicology Package APX3330 IND 6 Phase 1 Trials 5 Phase 2 Trials Phase 2 Trials Phase 3 Registration NDA Filing Focus on Ophthalmology Includes
ZETA-1 trial Previously developed by Eisai for hepatic inflammatory indications and by Apexian for solid tumors in 11 Phase 1 and 2 trials Extensively studied in over 20 in-vitro and animal studies with favorable efficacy and safety
results
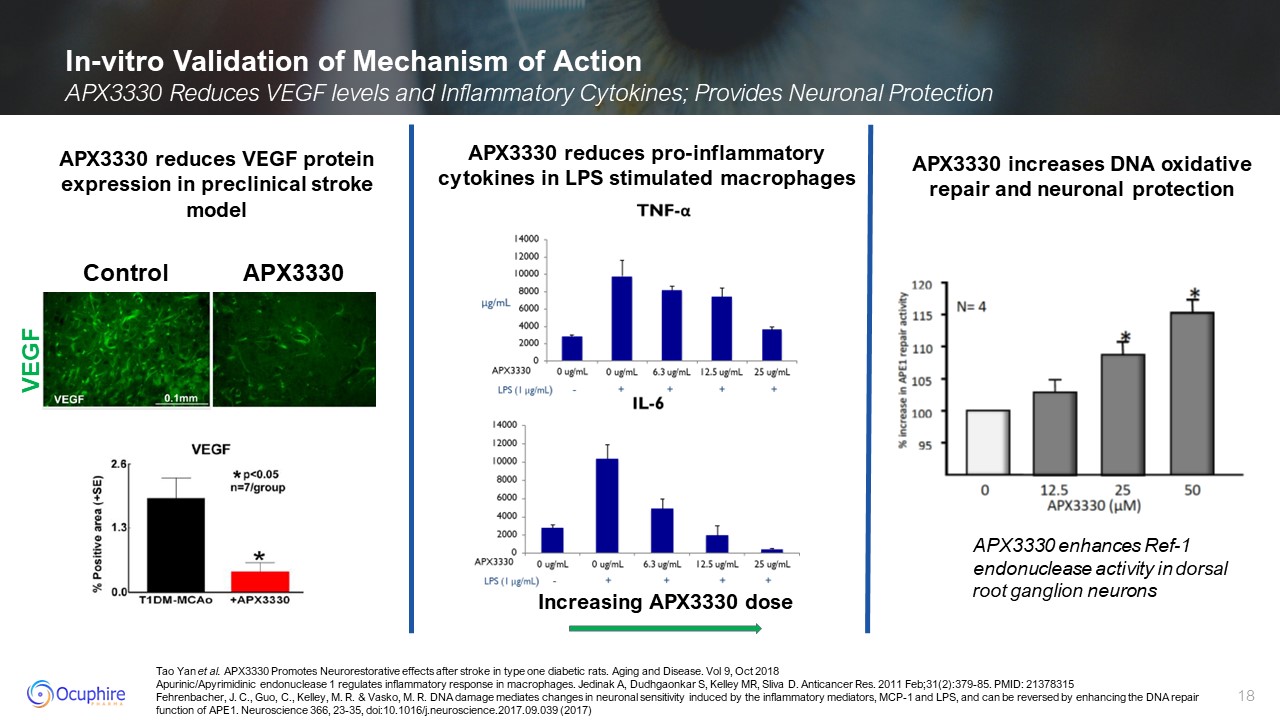
Tao Yan et al. APX3330 Promotes Neurorestorative effects after stroke in type
one diabetic rats. Aging and Disease. Vol 9, Oct 2018 Apurinic/Apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 regulates inflammatory response in macrophages. Jedinak A, Dudhgaonkar S, Kelley MR, Sliva D. Anticancer Res. 2011 Feb;31(2):379-85. PMID:
21378315 Fehrenbacher, J. C., Guo, C., Kelley, M. R. & Vasko, M. R. DNA damage mediates changes in neuronal sensitivity induced by the inflammatory mediators, MCP-1 and LPS, and can be reversed by enhancing the DNA repair function of
APE1. Neuroscience 366, 23-35, doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.09.039 (2017) In-vitro Validation of Mechanism of Action APX3330 Reduces VEGF levels and Inflammatory Cytokines; Provides Neuronal Protection APX3330 reduces VEGF protein
expression in preclinical stroke model APX3330 reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS stimulated macrophages Increasing APX3330 dose VEGF Control APX3330 APX3330 enhances Ref-1 endonuclease activity in dorsal root ganglion
neurons APX3330 increases DNA oxidative repair and neuronal protection
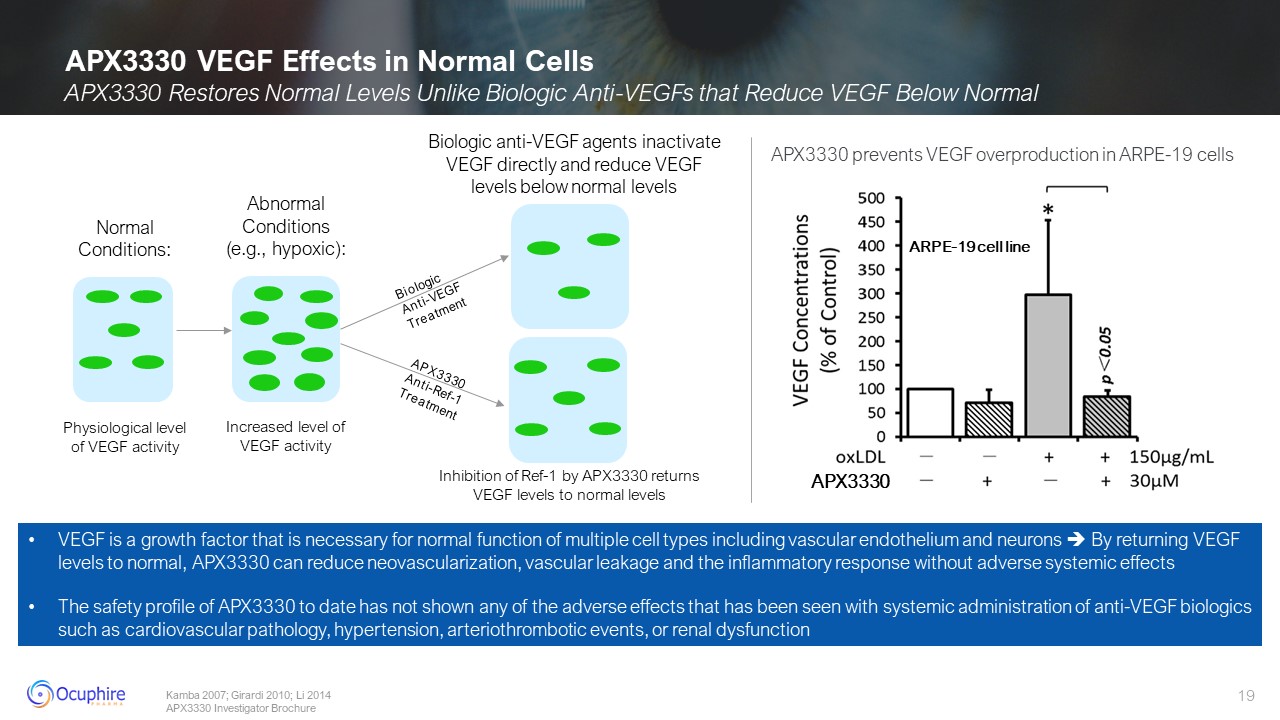
APX3330 VEGF Effects in Normal Cells Abnormal Conditions (e.g.,
hypoxic): Increased level of VEGF activity Normal Conditions: Physiological level of VEGF activity Kamba 2007; Girardi 2010; Li 2014 APX3330 Investigator Brochure Biologic Anti-VEGF Treatment APX3330 Anti-Ref-1 Treatment Biologic
anti-VEGF agents inactivate VEGF directly and reduce VEGF levels below normal levels Inhibition of Ref-1 by APX3330 returns VEGF levels to normal levels VEGF is a growth factor that is necessary for normal function of multiple cell types
including vascular endothelium and neurons By returning VEGF levels to normal, APX3330 can reduce neovascularization, vascular leakage and the inflammatory response without adverse systemic effects The safety profile of APX3330 to date
has not shown any of the adverse effects that has been seen with systemic administration of anti-VEGF biologics such as cardiovascular pathology, hypertension, arteriothrombotic events, or renal dysfunction APX3330 ARPE-19 cell
line APX3330 prevents VEGF overproduction in ARPE-19 cells APX3330 Restores Normal Levels Unlike Biologic Anti-VEGFs that Reduce VEGF Below Normal

APX3330 ZETA-1 Clinical Trial
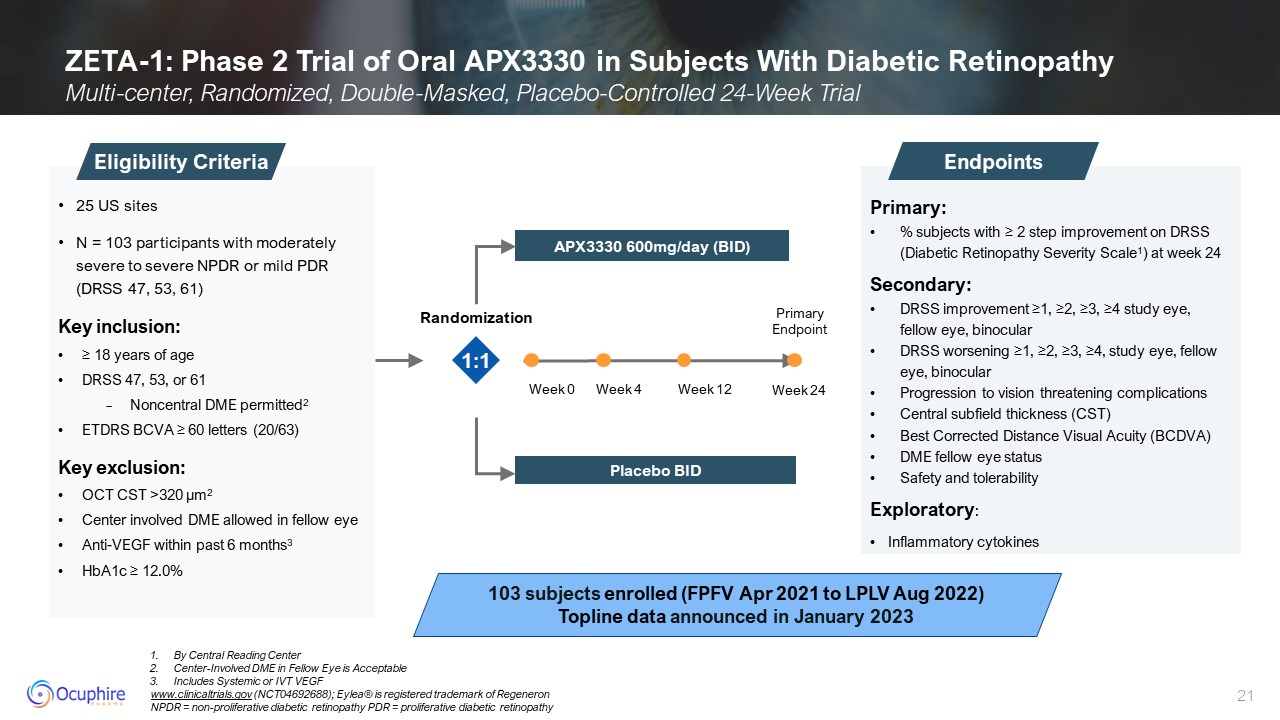
ZETA-1: Phase 2 Trial of Oral APX3330 in Subjects With Diabetic
Retinopathy Multi-center, Randomized, Double-Masked, Placebo-Controlled 24-Week Trial Primary: % subjects with ≥ 2 step improvement on DRSS (Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale1) at week 24 Secondary: DRSS improvement ≥1, ≥2, ≥3, ≥4
study eye, fellow eye, binocular DRSS worsening ≥1, ≥2, ≥3, ≥4, study eye, fellow eye, binocular Progression to vision threatening complications Central subfield thickness (CST) Best Corrected Distance Visual Acuity (BCDVA) DME fellow
eye status Safety and tolerability Exploratory: Inflammatory cytokines Endpoints 25 US sites N = 103 participants with moderately severe to severe NPDR or mild PDR (DRSS 47, 53, 61) Key inclusion: ≥ 18 years of age DRSS 47, 53, or
61 Noncentral DME permitted2 ETDRS BCVA ≥ 60 letters (20/63) Key exclusion: OCT CST >320 µm2 Center involved DME allowed in fellow eye Anti-VEGF within past 6 months3 HbA1c ≥ 12.0% Eligibility Criteria 103 subjects enrolled (FPFV
Apr 2021 to LPLV Aug 2022) Topline data announced in January 2023 1:1 By Central Reading Center Center-Involved DME in Fellow Eye is Acceptable Includes Systemic or IVT VEGF www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04692688); Eylea® is registered
trademark of Regeneron NPDR = non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy PDR = proliferative diabetic retinopathy Week 0 Week 12 Week 24 Week 4 Primary Endpoint APX3330 600mg/day (BID) Placebo BID Randomization
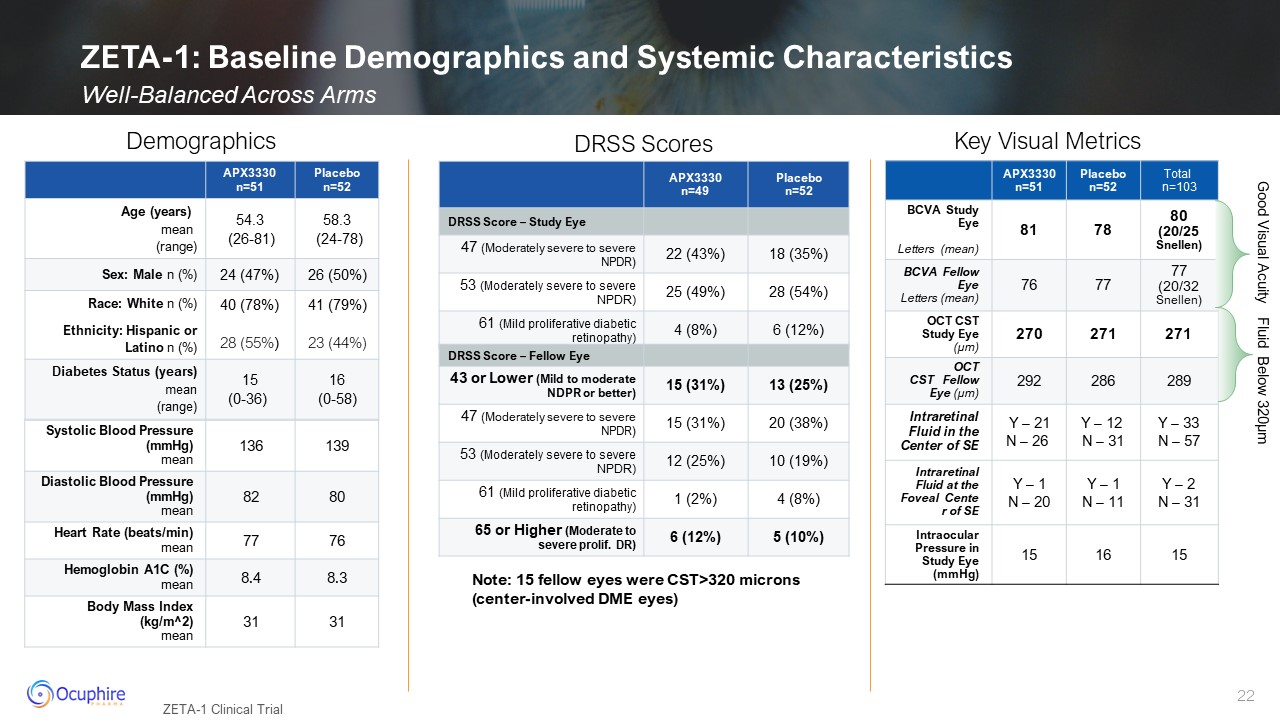
ZETA-1: Baseline Demographics and Systemic Characteristics Well-Balanced Across
Arms ZETA-1 Clinical Trial APX3330 n=51 Placebo n=52 Age (years) mean (range) 54.3 (26-81) 58.3 (24-78) Sex: Male n (%) 24 (47%) 26 (50%) Race: White n (%) Ethnicity: Hispanic or Latino n (%) 40 (78%) 28
(55%) 41 (79%) 23 (44%) Diabetes Status (years) mean (range) 15(0-36) 16(0-58) Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mean 136 139 Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) mean 82 80 Heart Rate (beats/min) mean 77 76 Hemoglobin A1C
(%)mean 8.4 8.3 Body Mass Index (kg/m^2)mean 31 31 Demographics DRSS Scores APX3330 n=51 Placebo n=52 Total n=103 BCVA Study Eye Letters (mean) 81 78 80(20/25 Snellen) BCVA Fellow Eye Letters (mean) 76 77 77(20/32
Snellen) OCT CST Study Eye (µm) 270 271 271 OCT CST Fellow Eye (µm) 292 286 289 Intraretinal Fluid in the Center of SE Y – 21 N – 26 Y – 12 N – 31 Y – 33 N – 57 Intraretinal Fluid at the Foveal Center of SE Y – 1 N –
20 Y – 1 N – 11 Y – 2 N – 31 Intraocular Pressure in Study Eye (mmHg) 15 16 15 APX3330 n=49 Placebo n=52 DRSS Score – Study Eye 47 (Moderately severe to severe NPDR) 22 (43%) 18 (35%) 53 (Moderately severe to
severe NPDR) 25 (49%) 28 (54%) 61 (Mild proliferative diabetic retinopathy) 4 (8%) 6 (12%) DRSS Score – Fellow Eye 43 or Lower (Mild to moderate NDPR or better) 15 (31%) 13 (25%) 47 (Moderately severe to severe NPDR) 15
(31%) 20 (38%) 53 (Moderately severe to severe NPDR) 12 (25%) 10 (19%) 61 (Mild proliferative diabetic retinopathy) 1 (2%) 4 (8%) 65 or Higher (Moderate to severe prolif. DR) 6 (12%) 5 (10%) Key Visual Metrics Good Visual
Acuity Fluid Below 320µm Note: 15 fellow eyes were CST>320 microns (center-involved DME eyes)
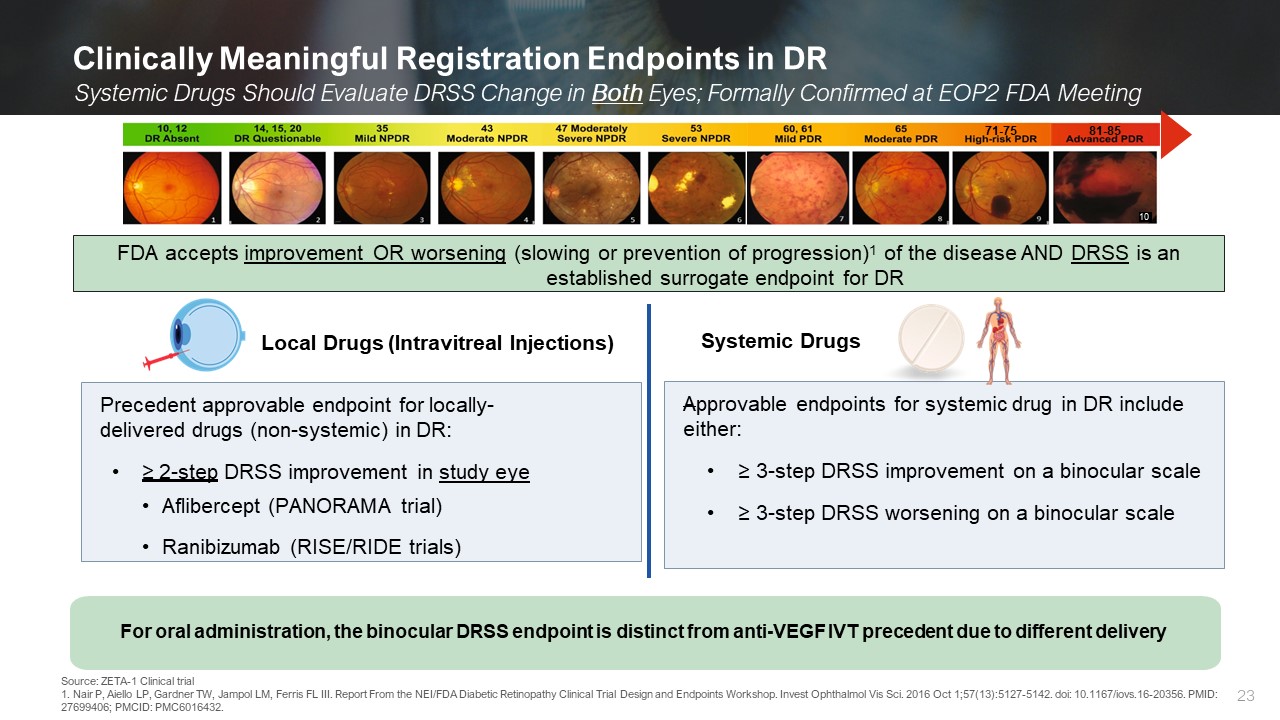
Clinically Meaningful Registration Endpoints in DR Systemic Drugs Should
Evaluate DRSS Change in Both Eyes; Formally Confirmed at EOP2 FDA Meeting Source: ZETA-1 Clinical trial 1. Nair P, Aiello LP, Gardner TW, Jampol LM, Ferris FL III. Report From the NEI/FDA Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Trial Design and
Endpoints Workshop. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Oct 1;57(13):5127-5142. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20356. PMID: 27699406; PMCID: PMC6016432. 10 81-85 71-75 Local Drugs (Intravitreal Injections) Systemic Drugs Precedent approvable endpoint
for locally- delivered drugs (non-systemic) in DR: ≥ 2-step DRSS improvement in study eye Aflibercept (PANORAMA trial) Ranibizumab (RISE/RIDE trials) Approvable endpoints for systemic drug in DR include either: ≥ 3-step DRSS improvement
on a binocular scale ≥ 3-step DRSS worsening on a binocular scale For oral administration, the binocular DRSS endpoint is distinct from anti-VEGF IVT precedent due to different delivery FDA accepts improvement OR worsening (slowing or
prevention of progression)1 of the disease AND DRSS is an established surrogate endpoint for DR

End-of-Phase 2 Meeting Outcome
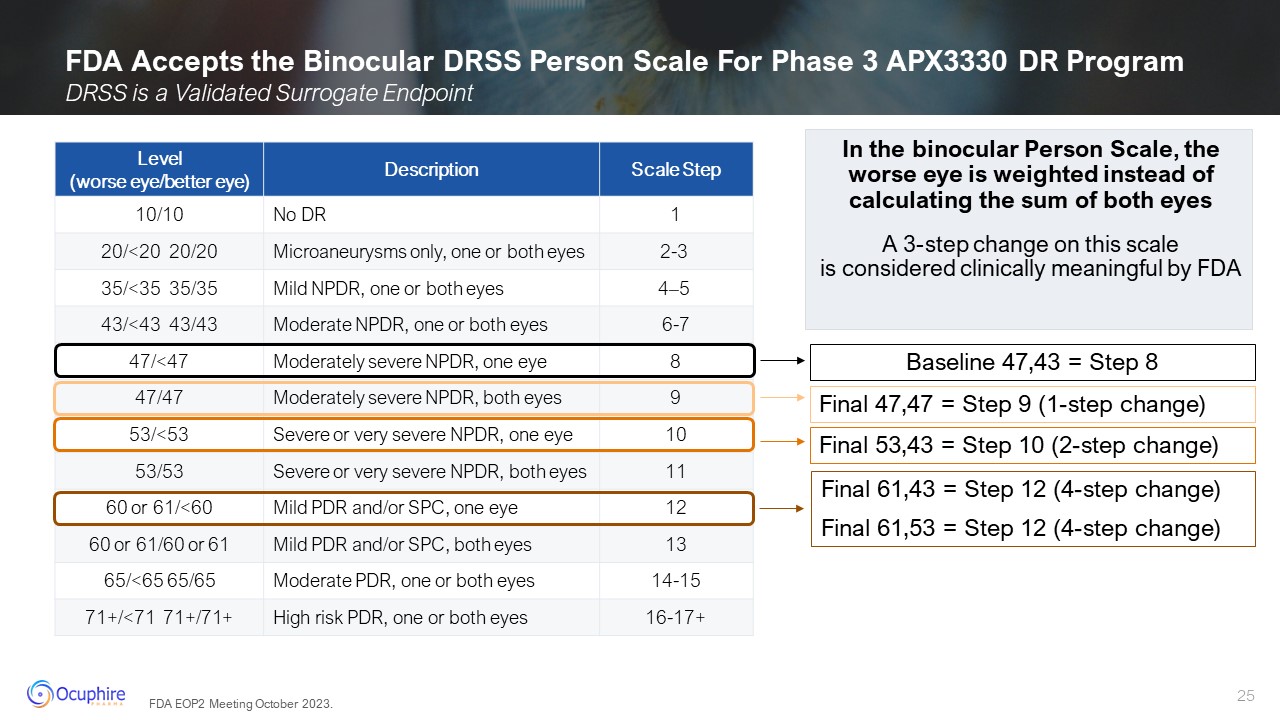
FDA Accepts the Binocular DRSS Person Scale For Phase 3 APX3330 DR
Program In the binocular Person Scale, the worse eye is weighted instead of calculating the sum of both eyes A 3-step change on this scale is considered clinically meaningful by FDA Level (worse eye/better eye) Description Scale
Step 10/10 No DR 1 20/<20 20/20 Microaneurysms only, one or both eyes 2-3 35/<35 35/35 Mild NPDR, one or both eyes 4–5 43/<43 43/43 Moderate NPDR, one or both eyes 6-7 47/<47 Moderately severe NPDR, one
eye 8 47/47 Moderately severe NPDR, both eyes 9 53/<53 Severe or very severe NPDR, one eye 10 53/53 Severe or very severe NPDR, both eyes 11 60 or 61/<60 Mild PDR and/or SPC, one eye 12 60 or 61/60 or 61 Mild PDR and/or
SPC, both eyes 13 65/<65 65/65 Moderate PDR, one or both eyes 14-15 71+/<71 71+/71+ High risk PDR, one or both eyes 16-17+ DRSS is a Validated Surrogate Endpoint Baseline 47,43 = Step 8 Final 53,43 = Step 10 (2-step change)
Final 61,43 = Step 12 (4-step change) Final 61,53 = Step 12 (4-step change) Final 47,47 = Step 9 (1-step change) FDA EOP2 Meeting October 2023.
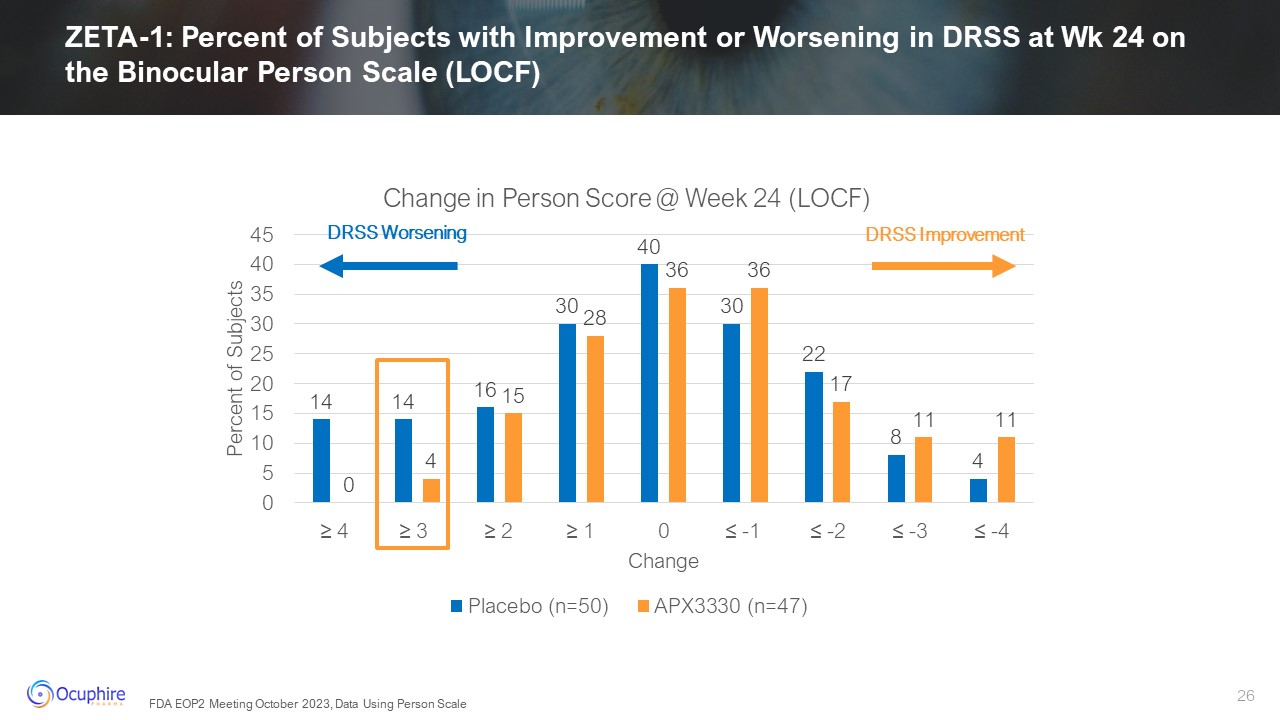
DRSS Worsening DRSS Improvement ZETA-1: Percent of Subjects with Improvement
or Worsening in DRSS at Wk 24 on the Binocular Person Scale (LOCF) FDA EOP2 Meeting October 2023, Data Using Person Scale
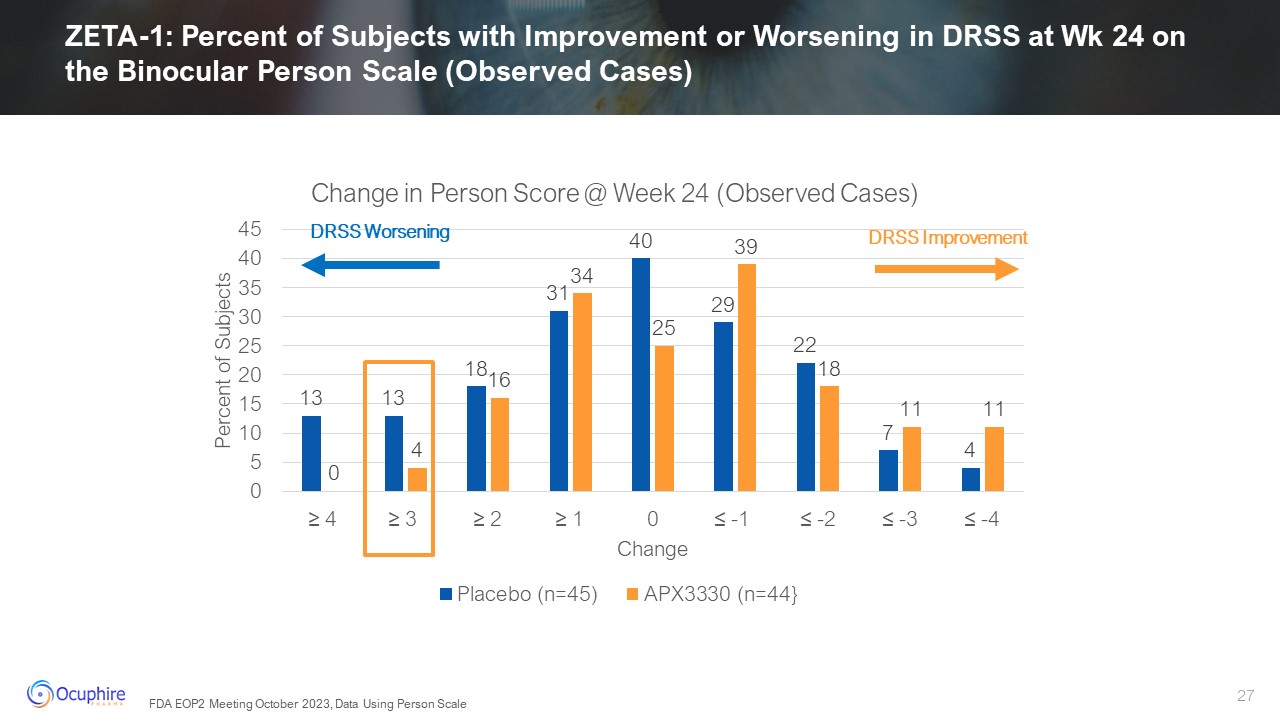
ZETA-1: Percent of Subjects with Improvement or Worsening in DRSS at Wk 24 on
the Binocular Person Scale (Observed Cases) DRSS Improvement DRSS Worsening FDA EOP2 Meeting October 2023, Data Using Person Scale
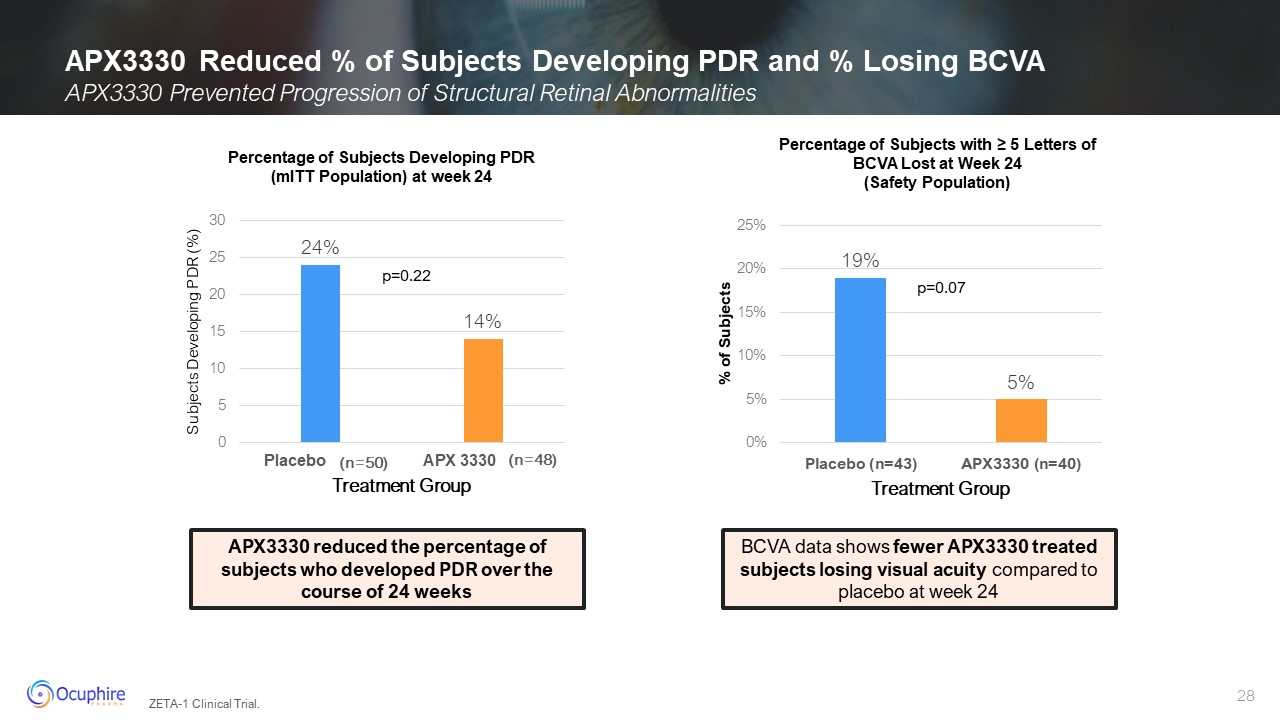
APX3330 Reduced % of Subjects Developing PDR and % Losing BCVA Percentage of
Subjects Developing PDR (mITT Population) at week 24 APX3330 reduced the percentage of subjects who developed PDR over the course of 24 weeks Percentage of Subjects with ≥ 5 Letters of BCVA Lost at Week 24 (Safety Population) BCVA data
shows fewer APX3330 treated subjects losing visual acuity compared to placebo at week 24 ZETA-1 Clinical Trial. APX3330 Prevented Progression of Structural Retinal Abnormalities
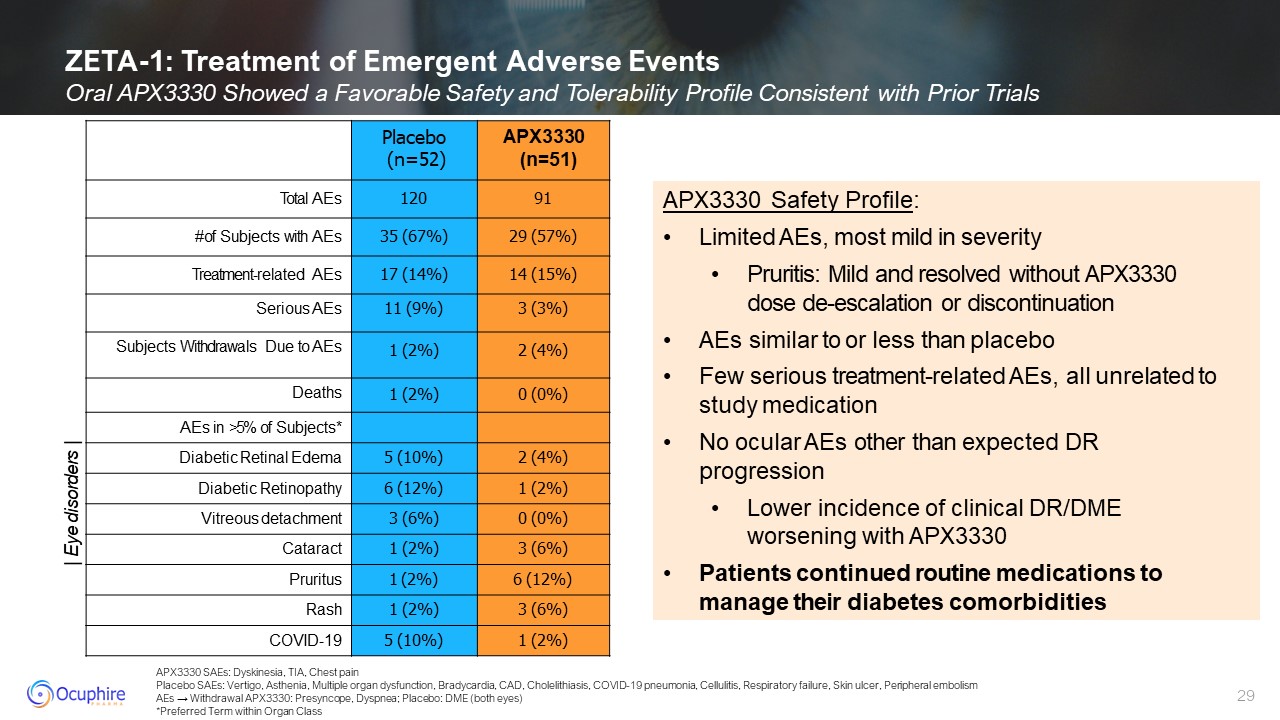
APX3330 SAEs: Dyskinesia, TIA, Chest pain Placebo SAEs: Vertigo, Asthenia,
Multiple organ dysfunction, Bradycardia, CAD, Cholelithiasis, COVID-19 pneumonia, Cellulitis, Respiratory failure, Skin ulcer, Peripheral embolism AEs → Withdrawal APX3330: Presyncope, Dyspnea; Placebo: DME (both eyes) *Preferred Term
within Organ Class ZETA-1: Treatment of Emergent Adverse Events Oral APX3330 Showed a Favorable Safety and Tolerability Profile Consistent with Prior Trials Placebo (n=52) APX3330 (n=51) Total AEs 120 91 # of Subjects with AEs 35
(67%) 29 (57%) Treatment-related AEs 17 (14%) 14 (15%) Serious AEs 11 (9%) 3 (3%) Subjects Withdrawals Due to AEs 1 (2%) 2 (4%) Deaths 1 (2%) 0 (0%) AEs in >5% of Subjects* Diabetic Retinal Edema 5 (10%) 2 (4%) Diabetic
Retinopathy 6 (12%) 1 (2%) Vitreous detachment 3 (6%) 0 (0%) Cataract 1 (2%) 3 (6%) Pruritus 1 (2%) 6 (12%) Rash 1 (2%) 3 (6%) COVID-19 5 (10%) 1 (2%) APX3330 Safety Profile: Limited AEs, most mild in severity Pruritis:
Mild and resolved without APX3330 dose de-escalation or discontinuation AEs similar to or less than placebo Few serious treatment-related AEs, all unrelated to study medication No ocular AEs other than expected DR progression Lower
incidence of clinical DR/DME worsening with APX3330 Patients continued routine medications to manage their diabetes comorbidities | Eye disorders |

APX3330 Summary Successful EOP2 FDA meeting completed in October 2023;
agreement that a 3-step change on the binocular person scale is an approvable registration endpoint Submit Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) Advance APX3330 into Phase 3 program with long-term exposure (up to 2 years) APX3330
Milestones To have a clinically meaningful impact on slowing or preventing progression to reduce likelihood of vision loss in diabetic retinopathy patients Our Goal for Patients 30

DR is one of the largest markets in retina with 10M patients in US and over 100M
worldwide Majority of the NPDR patients are not candidates for approved biologics treatments and are left untreated APX3330 first-in-class oral drug with unique MOA that inhibits Ref-1 which reduces VEGF and inflammatory cytokines to normal
physiological levels Prevention of worsening is a clinically meaningful potential registration endpoint APX3330 demonstrated favorable safety and tolerability in diabetic patients Successful EOP2 meeting with the FDA and a Special
Protocol Assessment (SPA) to be submitted APX3330 has the potential to be an early, non-invasive preventative treatment for the 8 million NPDR patients with the potential to treat other organs affected by diabetes (e.g., kidney disease,
peripheral neuropathy) Broad prescriber base including general ophthalmology, optometry and primary care due to favorable safety DR and APX3330 Key Takeaways

Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75%
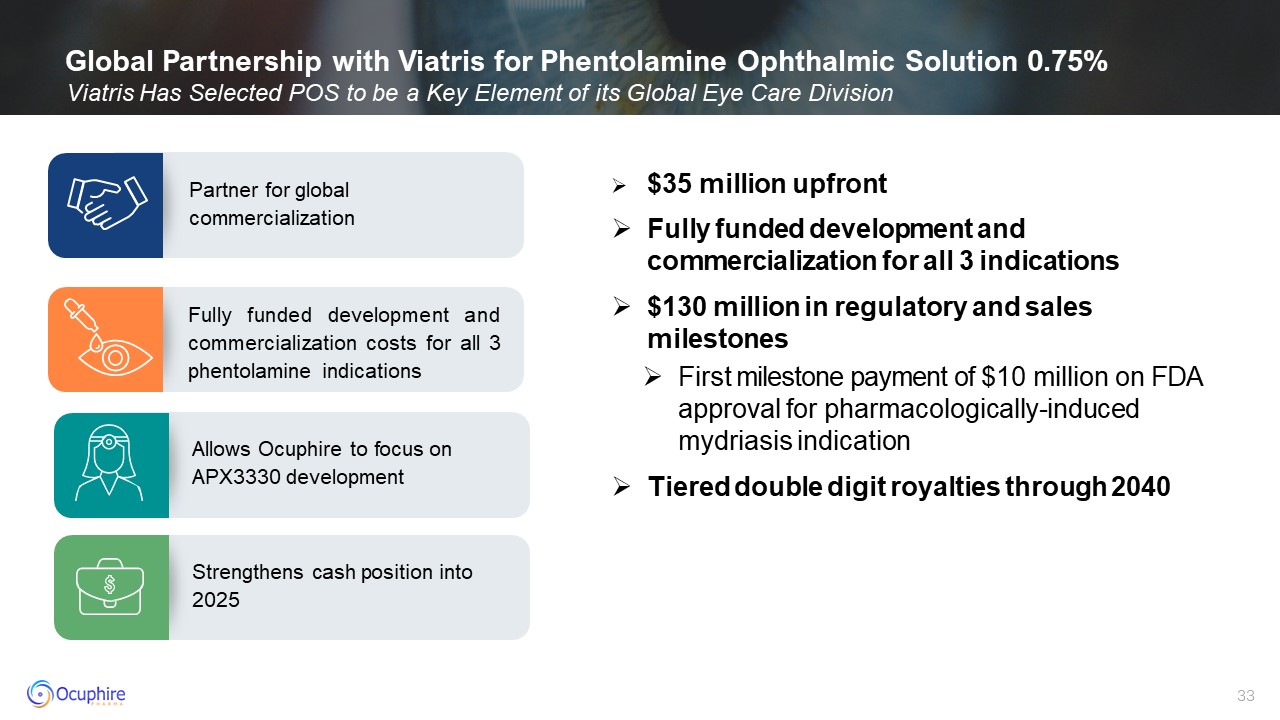
Global Partnership with Viatris for Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75%
Viatris Has Selected POS to be a Key Element of its Global Eye Care Division Fully funded development and commercialization costs for all 3 phentolamine indications Partner for global commercialization Allows Ocuphire to focus on
APX3330 development Strengthens cash position into 2025 $35 million upfront Fully funded development and commercialization for all 3 indications $130 million in regulatory and sales milestones First milestone payment of $10 million on
FDA approval for pharmacologically-induced mydriasis indication Tiered double digit royalties through 2040
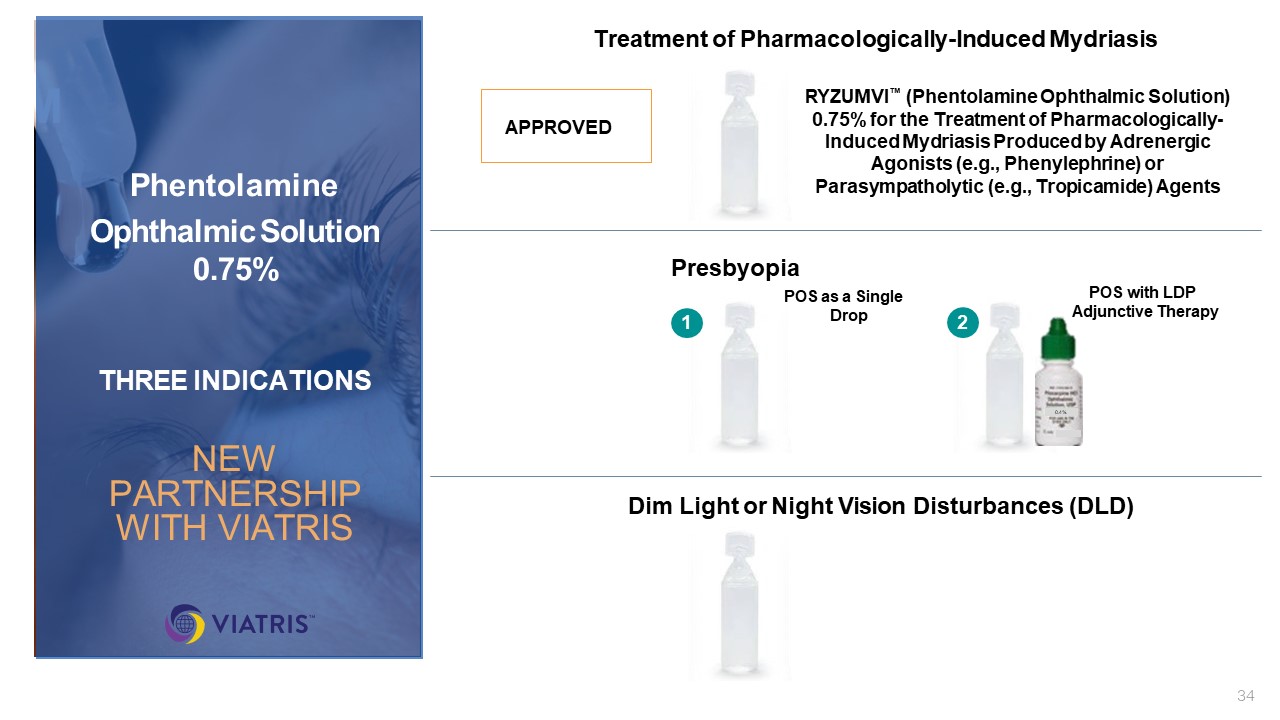
Treatment of Pharmacologically-Induced Mydriasis P DLD Presbyopia Dim Light
or Night Vision Disturbances (DLD) POS as a Single Drop POS with LDP Adjunctive Therapy 1 0.4% 2 RM Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% THREE INDICATIONS NEW PARTNERSHIP WITH VIATRIS APPROVED RYZUMVl™ (Phentolamine Ophthalmic
Solution) 0.75% for the Treatment of Pharmacologically-Induced Mydriasis Produced by Adrenergic Agonists (e.g., Phenylephrine) or Parasympatholytic (e.g., Tropicamide) Agents
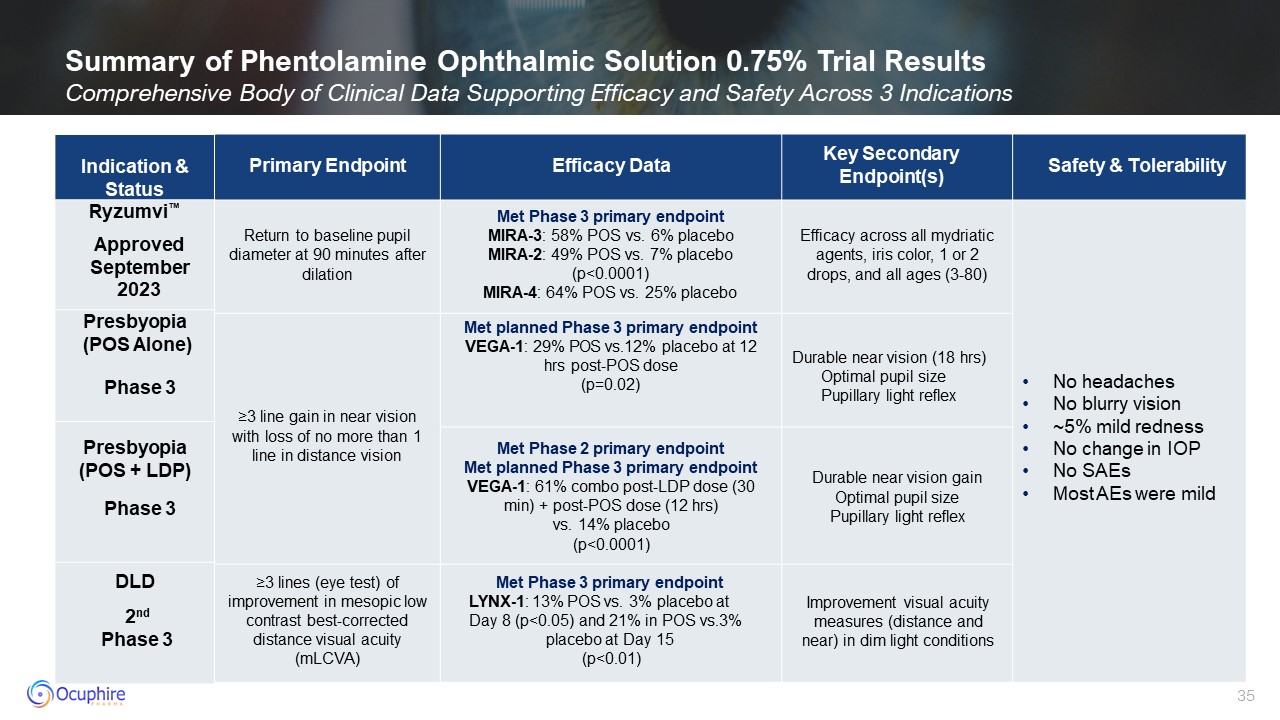
Summary of Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% Trial Results Comprehensive
Body of Clinical Data Supporting Efficacy and Safety Across 3 Indications Primary Endpoint Efficacy Data Key Secondary Endpoint(s) Safety & Tolerability Return to baseline pupil diameter at 90 minutes after dilation Met Phase 3
primary endpoint MIRA-3: 58% POS vs. 6% placebo MIRA-2: 49% POS vs. 7% placebo (p<0.0001) MIRA-4: 64% POS vs. 25% placebo Efficacy across all mydriatic agents, iris color, 1 or 2 drops, and all ages (3-80) No headaches No blurry
vision ~5% mild redness No change in IOP No SAEs Most AEs were mild ≥3 line gain in near vision with loss of no more than 1 line in distance vision Met planned Phase 3 primary endpoint VEGA-1: 29% POS vs.12% placebo at 12 hrs post-POS
dose (p=0.02) Durable near vision (18 hrs) Optimal pupil size Pupillary light reflex Met Phase 2 primary endpoint Met planned Phase 3 primary endpoint VEGA-1: 61% combo post-LDP dose (30 min) + post-POS dose (12 hrs) vs. 14% placebo
(p<0.0001) Durable near vision gain Optimal pupil size Pupillary light reflex ≥3 lines (eye test) of improvement in mesopic low contrast best-corrected distance visual acuity (mLCVA) Met Phase 3 primary endpoint LYNX-1: 13% POS vs. 3%
placebo at Day 8 (p<0.05) and 21% in POS vs.3% placebo at Day 15 (p<0.01) Improvement visual acuity measures (distance and near) in dim light conditions RM DLD Indication & Status Ryzumvi™ Presbyopia (POS Alone) Presbyopia
(POS + LDP) DLD 2nd Phase 3 Phase 3 Phase 3 Approved September 2023

Corporate Highlights Strong Financial Position to Fund Operations into
2025 Late-Stage Retinal Pipeline Represents Multi-Billion Dollar Opportunity in Unmet NPDR Patients Global License Agreement with Viatris to Fund Development and Commercialization of Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% for All Refractive
Indications APX Pipeline Driven by a Paradigm Changing, Dual Target Ref-1 Platform for Retinal Diseases APX3330 – Novel, Non-Invasive, Safe Oral Tablet to Treat Diabetic Retinopathy
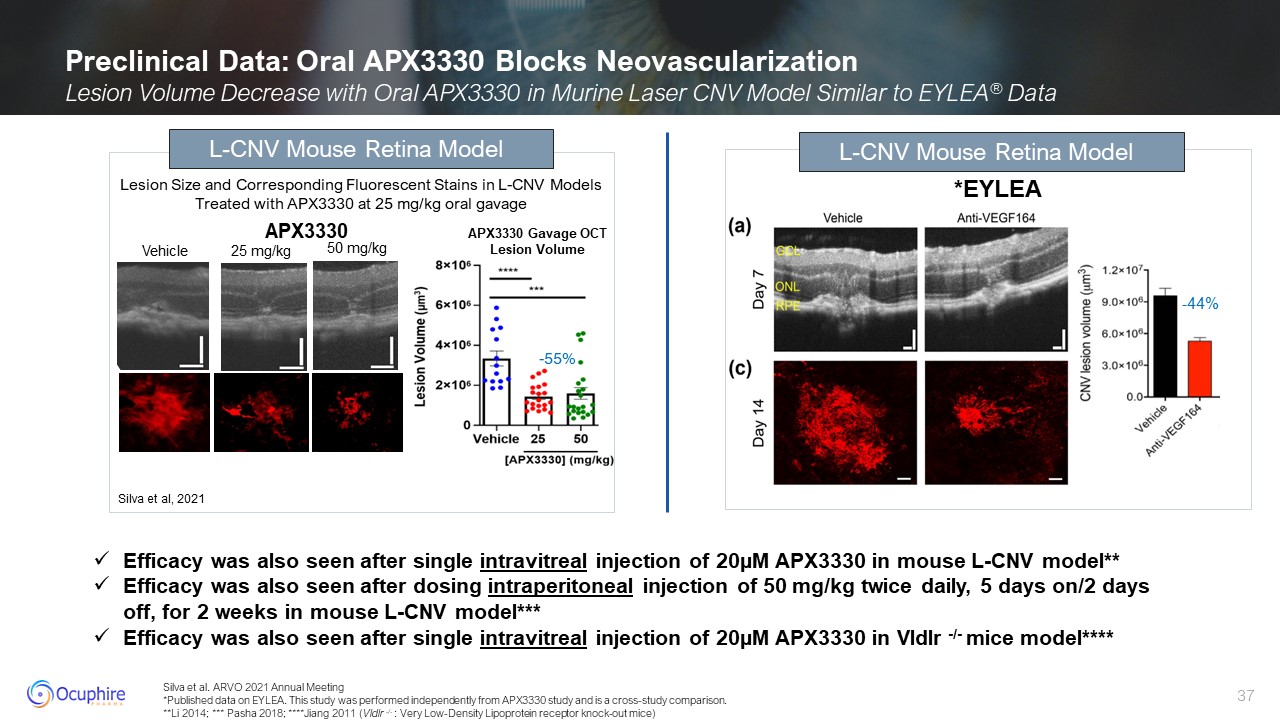
Silva et al. ARVO 2021 Annual Meeting *Published data on EYLEA. This study was
performed independently from APX3330 study and is a cross-study comparison. **Li 2014; *** Pasha 2018; ****Jiang 2011 (Vldlr -/- : Very Low-Density Lipoprotein receptor knock-out mice) Preclinical Data: Oral APX3330 Blocks
Neovascularization Lesion Volume Decrease with Oral APX3330 in Murine Laser CNV Model Similar to EYLEA® Data *EYLEA Lesion Size and Corresponding Fluorescent Stains in L-CNV Models Treated with APX3330 at 25 mg/kg oral gavage -55% L-CNV
Mouse Retina Model Silva et al, 2021 Vehicle 25 mg/kg 50 mg/kg APX3330 Gavage OCT Lesion Volume L-CNV Mouse Retina Model APX3330 Efficacy was also seen after single intravitreal injection of 20µM APX3330 in mouse L-CNV
model** Efficacy was also seen after dosing intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/kg twice daily, 5 days on/2 days off, for 2 weeks in mouse L-CNV model*** Efficacy was also seen after single intravitreal injection of 20µM APX3330 in Vldlr -/-
mice model**** -44%

Restore Vision & Clarity www.ocuphire.com ir@ocuphire.com Ocuphire
Pharma Appendix 38
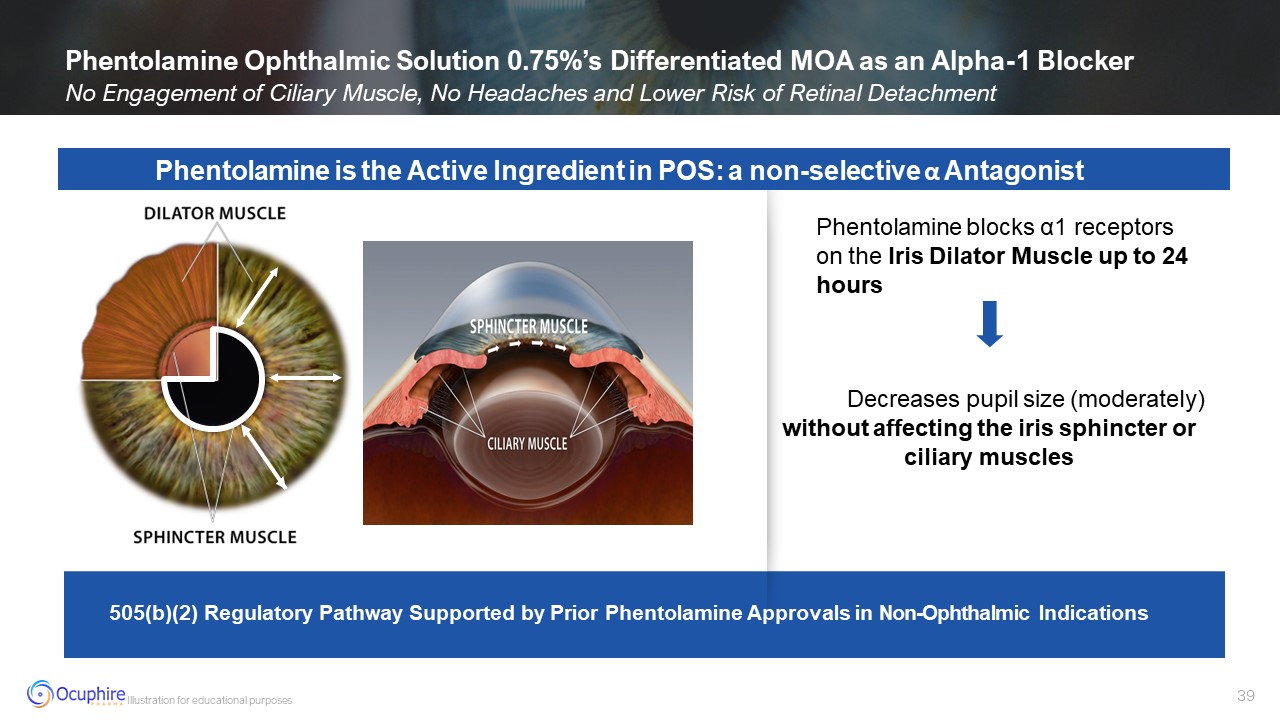
Decreases pupil size (moderately) without affecting the iris sphincter or
ciliary muscles 505(b)(2) Regulatory Pathway Supported by Prior Phentolamine Approvals in Non-Ophthalmic Indications Illustration for educational purposes Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75%’s Differentiated MOA as an Alpha-1
Blocker No Engagement of Ciliary Muscle, No Headaches and Lower Risk of Retinal Detachment Phentolamine is the Active Ingredient in POS: a non-selective α Antagonist Phentolamine blocks α1 receptors on the Iris Dilator Muscle up to 24
hours
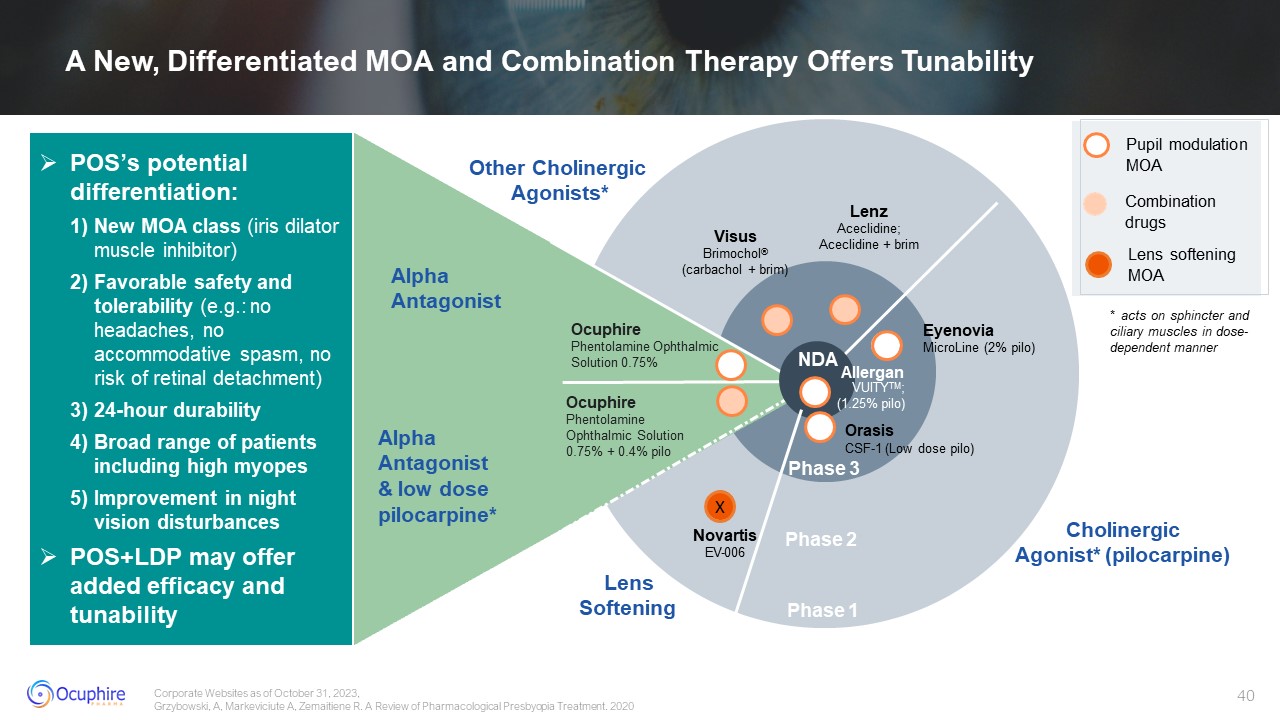
Phase 2 Phase 1 Ocuphire Phentolamine Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% + 0.4%
pilo Visus Brimochol® (carbachol + brim) Other Cholinergic Agonists* Cholinergic Agonist* (pilocarpine) Lenz Aceclidine; Aceclidine + brim Eyenovia MicroLine (2% pilo) Alpha Antagonist & low dose pilocarpine* Alpha
Antagonist NDA Allergan VUITYTM; (1.25% pilo) Orasis CSF-1 (Low dose pilo) Phase 3 POS’s potential differentiation: New MOA class (iris dilator muscle inhibitor) Favorable safety and tolerability (e.g.: no headaches, no
accommodative spasm, no risk of retinal detachment) 24-hour durability Broad range of patients including high myopes Improvement in night vision disturbances POS+LDP may offer added efficacy and tunability Ocuphire Phentolamine
Ophthalmic Solution 0.75% Pupil modulation MOA Combination drugs Lens softening MOA X Novartis EV-006 Lens Softening * acts on sphincter and ciliary muscles in dose- dependent manner Corporate Websites as of October 31, 2023,
Grzybowski, A, Markeviciute A, Zemaitiene R. A Review of Pharmacological Presbyopia Treatment. 2020 A New, Differentiated MOA and Combination Therapy Offers Tunability

Ocuphire's World-Class Medical Advisory Board Chief Medical Advisor, Ocuphire
Refractive Specialist Jay Pepose, MD, PhD UCLA School of Medicine Refractive Specialist Y. Ralph Chu, MD Northwestern University Refractive Specialist Zaina Al-Mohtaseb, MD Baylor College of Medicine Refractive Specialist James Katz, MD
University of Illinois Refractive Specialist Marguerite McDonald, MD Columbia University Refractive Specialist Mitch Jackson, MD University of Chicago Refractive/ Glaucoma Specialist Thomas Samuelson, MD University of
Minnesota Refractive/Glaucoma Specialist Inder Paul Singh, MD The Chicago Medical School Eliot Lazar, MD Georgetown University elCON Medical Retinal Specialist Peter Kaiser, MD Harvard Medical School Retinal Specialist David Lally, MD
Vanderbilt University Retinal Specialist Michael Allingham, MD, PhD University of North Carolina Retinal Specialist David Boyer, MD Chicago Medical School Retinal Specialist David Brown, MD Baylor University Retinal Specialist Jeffrey
Heier, MD Boston University Retinal Specialist Anat Lowenstein, MD, PhD The Hebrew University Retinal Specialist Caroline Baumal, MD University of Toronto Medical School Optometry Douglas Devries, OD University of
Nevada Optometry Paul Karpecki, OD Indiana University Optometry Justin Schweitzer, OD Pacific University College of Optometry Optometry Selina McGee, OD Northeastern State University Optometry Leslie O’Dell, OD Salus
University Co-Founder Apexian/APX3330 Mark Kelley, PhD Indiana University

Ocuphire Board of Directors Sean Ainsworth, MBA Lead Independent Director,
Board Director Jay Pepose, MD, PhD Board Director Susan Benton, MBA Board Director Cam Gallagher, MBA Chair, Board Director James Manuso, PhD/MBA Board Director Richard Rodgers, MBA Board Director George Magrath, MD, MBA
CEO & Board Director